How to Become Security Engineer after doing Pent Certification

Cyber threats overshadow everything in this constantly changing digital world. Therefore, the position of a security engineer has become unavoidable. These security engineers are the defenders of our online strongholds. Additionally, the designers of solid security networks, and the first line of defense against cyber threats. But what does it take to be a security engineer? What skills are mandatory, and how do you navigate this ever-changing career path? This blog will demystify the world of security engineering, providing a comprehensive guide to the roles, responsibilities, and steps to success, and how Orbus CyberSec Trainings can be your launchpad into this vital field.
What is a Security Engineer?
A security engineer is the digital architect. They build and maintain an organization’s defenses against cyber threats. Additionally, they proactively seek out vulnerabilities. These security engineers updates software, configures firewalls, and implement encryption. Additionally, they even simulate attacks through penetration testing to find weaknesses before hackers do. Furthermore, you will find them with titles like cybersecurity or cloud cyber security engineer. When breaches occur, these security engineers become digital first responders. They analyze damage and develop recovery plans. These individuals are problem-solvers, communicators, and strategists. They also ensure data safety and system integrity.
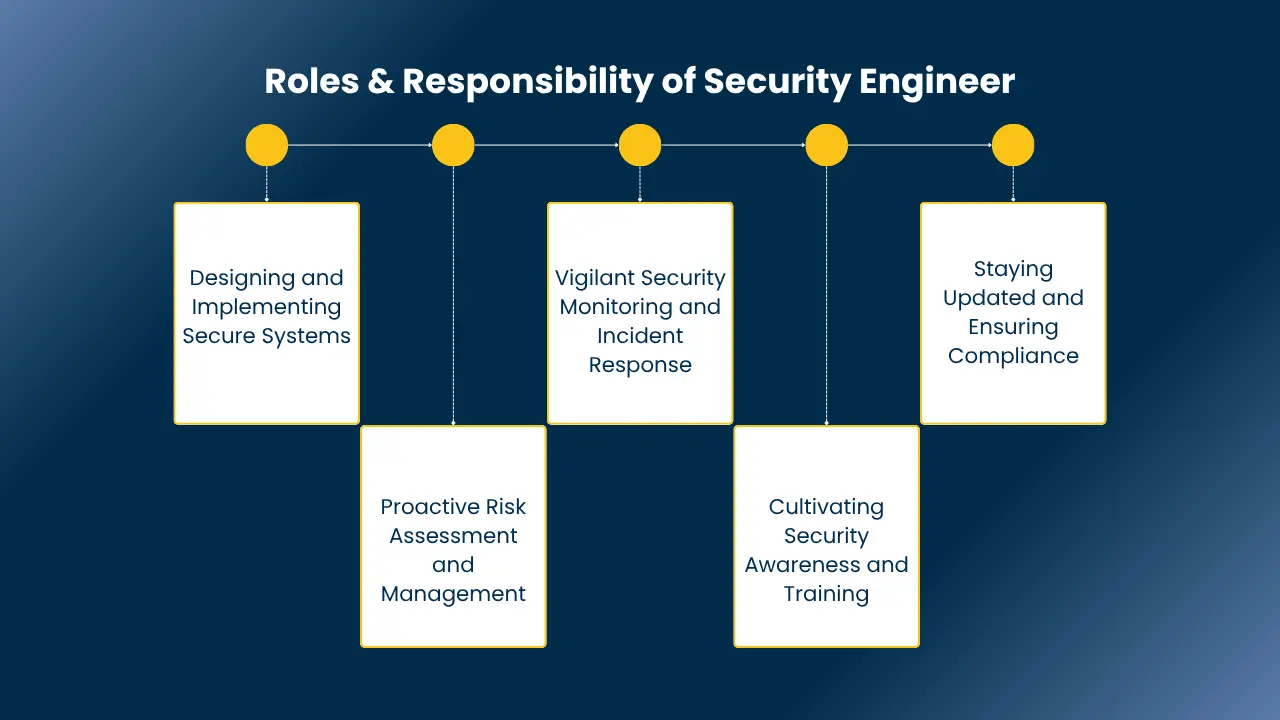
Roles & Responsibility of Security Engineer
Security engineers are the digital guardians. These penetration testing companies in India are responsible for safeguarding an organization’s data and systems. These individuals blend technical expertise with proactive strategies. They also build and maintain a robust penetration testing in cyber security posture.
1. Designing and Implementing Secure Systems
Security engineers are the architects of digital safety. They craft security policies, design secure network architectures, and implement critical security technologies. These technologies includes firewalls and encryption tools. Additionally, they react to threats and build a digital fortress to protect an organization’s vital data and systems.
2. Proactive Risk Assessment and Management
These professionals conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats. Additionally these security engineers also develop and implement risk mitigation plans. They also help organizations to stay ahead of emerging security threats and ensure the organization is prepared for any eventuality.
3. Vigilant Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Security engineers are the vigilant guards, constantly monitoring systems and networks for suspicious activity. When security incidents do occur, they respond swiftly, containing the damage, eradicating the threat, and recovering the affected systems. They analyze security logs like detectives, piecing together clues to prevent future attacks.
4. Cultivating Security Awareness and Training
They’re not just tech experts; they’re educators. Security engineers foster a security-conscious culture by training staff on best practices and policies. They collaborate with IT, development, and operations teams, ensuring security is woven into every aspect of the organization.
5. Staying Updated and Ensuring Compliance
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving. Security engineers stay ahead of the game, keeping up with the latest threats and technologies. They also participate in security audits and assessments, ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations.
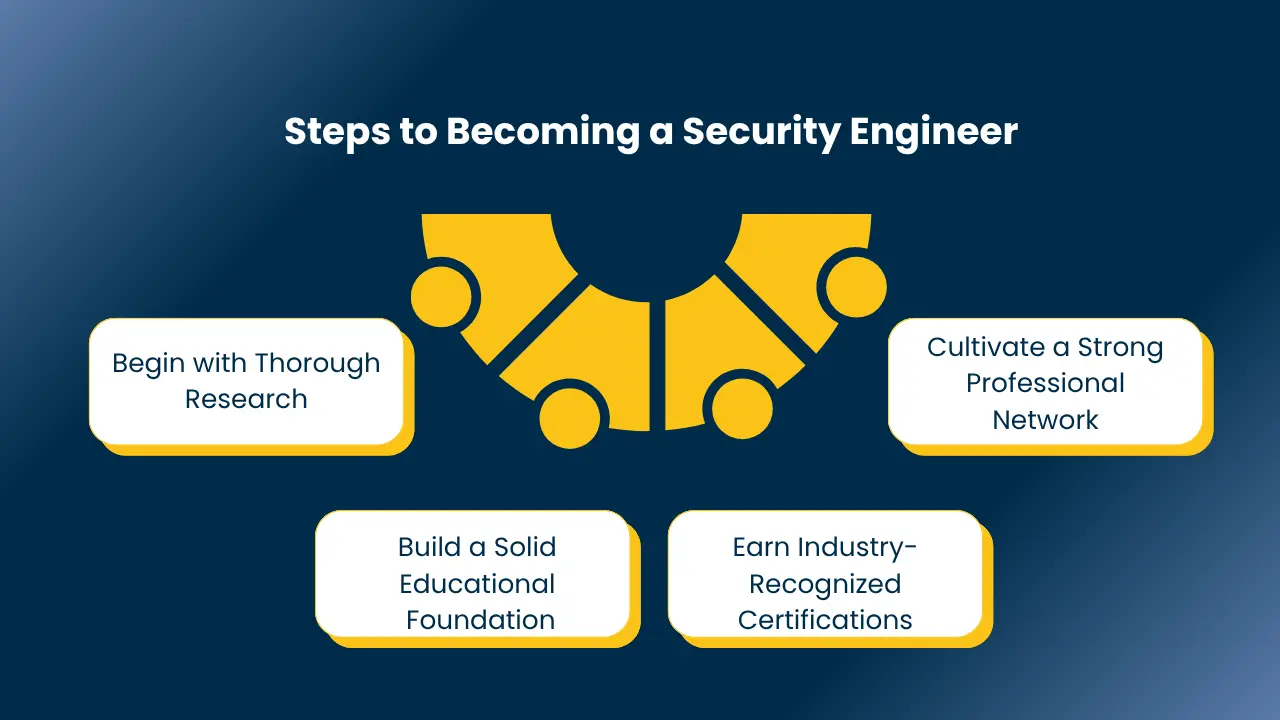
Steps to Becoming a Security Engineer
Becoming a security engineer means stepping into a dynamic and crucial role, safeguarding digital assets and defending against cyber threats. It’s a career path that demands a blend of technical skill, strategic thinking, and a passion for problem-solving. Here’s a practical roadmap to help you navigate this exciting field.
1. Begin with Thorough Research
Start by exploring the landscape. Understand the diverse roles security engineers play, from conducting security audits to developing incident response plans. Research the specific skills and certifications employers value. This initial step will help you tailor your learning journey and set clear career goals.
2. Build a Solid Educational Foundation
A strong educational background is essential. While some roles may accept associate degrees, many require a bachelor’s in cybersecurity, computer science, or a related field. Consider specializing with a cybersecurity emphasis to gain targeted knowledge. For advanced positions, a master’s or Ph.D. can significantly enhance your prospects. Remember, education is not just about degrees; it’s about building a robust understanding of security principles.
3. Earn Industry-Recognized Certifications
Certifications are your proof of expertise. In the cybersecurity field, they demonstrate your proficiency in specialized areas. Invest in certifications that align with your career goals and industry demands. They validate your skills and make you a more competitive candidate.
4. Cultivate a Strong Professional Network
Networking is key. Connect with professionals in the cybersecurity community, attend industry events, and engage in online forums. Building relationships can open doors to job opportunities, mentorship, and valuable insights. Your network is your lifeline to staying informed and advancing in your career.
Security Engineer Skills and Experience
Stepping into the role of a security engineer demands a unique blend of technical mastery and strategic insight. It’s not just about knowing the latest security tools; it’s about understanding the evolving threat landscape and anticipating future challenges. Here’s a look at the essential skills and experiences that shape a successful security engineer.

1. Strong Technical Foundation and Education
Typically, a security engineer starts with a solid educational base, often a bachelor’s degree or higher in computer engineering, cybersecurity, or information security. This foundation provides a deep understanding of core concepts like risk assessment, network architecture, and digital forensics. They stay current with the latest advancements in virus detection, firewall technology, and content filtering, ensuring they’re equipped to handle emerging threats.
2. Proficiency in Code Analysis and Vulnerability Detection
A key skill is the ability to analyze code, spotting anomalies and malicious lines that could create security vulnerabilities. They think like hackers, understanding how exploits work, to better defend against them. This involves not just recognizing dangerous code, but also understanding how to mitigate it effectively.
3. Communication and Collaboration Skills
Beyond technical prowess, security engineers are excellent communicators. They translate complex security issues into understandable language for colleagues and management, facilitating informed decision-making. Collaboration is also crucial, as they work closely with various teams to integrate security into every aspect of the organization.
Industry Certifications and Security Clearances
Many roles require industry penetration testing certifications like CISSP, CompTIA Security+, or Certified Ethical Hacker, validating their expertise. Some positions, particularly in government or sensitive sectors, may also require security clearances, demonstrating their trustworthiness and adherence to strict security protocols.
1. Practical Experience and Core Competencies
Employers look for hands-on experience in areas like risk assessment, vulnerability management, and incident response. They value skills in developing and implementing security policies, maintaining antivirus software, and detecting intrusions. Proficiency in scripting languages like Python and experience with cloud platforms like AWS are increasingly essential.
2. Anticipating Future Skills
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving. Security engineers must stay ahead of the curve, focusing on emerging areas like container security, cloud security, SaaS application security, and privileged account management. A comprehensive understanding of software security is also vital in today’s digital world.
Read More: What is Footprinting in Ethical Hacking? Which Tool is Best for You?
How Orbus Can Help You Became a Certified Security Engineer?
Orbus CyberSec Trainings focuses on giving you the practical skills needed to excel as a security engineer, especially in areas like finding vulnerabilities and testing security. Their CPENT training is a great way to gain these skills.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Course | EC-Council Certified Penetration Testing Expert (CPENT) |
| Focus | Advanced, hands-on penetration testing, crucial for security engineers. |
| Learning Outcomes |
|
| Duration | Intensive training days + 24-hour practical exam. (Contact Orbus CyberSec Trainings for specific dates.) |
| Fees | Variable. Contact Orbus CyberSec Trainings for current pricing. |
| Career Benefit | Practical vulnerability assessment skills, understanding attacker tactics, and CPENT certification credibility. |
Conclusion
Becoming a security engineer is a challenging yet rewarding journey. It requires a blend of technical expertise, problem-solving skills, and a commitment to staying ahead of the ever-evolving threat landscape. As we’ve explored, the path involves building a strong educational foundation, gaining practical experience, and earning industry-recognized certifications. Orbus CyberSec Trainings, with its focus on practical, hands-on training and the highly valuable penetration testing course, provides a significant advantage in developing the critical skills needed for this profession. Whether you’re just starting your cybersecurity career or looking to advance your skills, remember that the demand for skilled security engineers continues to grow. Embrace the challenge, stay curious, and you’ll be well on your way to a successful career in securing our digital world.
Understand how Orbus can help your career!
Speak with an Expert Now!
FAQ's
What qualifications do I need to be a security engineer?
Bachelor's degree in IT/CS, relevant certifications (like CPENT, OSCP, Security+), and practical experience.
What is the salary of Cpent certified person?
Variable, depending on experience and location. CPENT enhances earning potential due to advanced skills.
Is CPENT better than OSCP?
Different focuses. CPENT: enterprise networks; OSCP: individual system exploitation. Both are highly respected.
Cyber security engineer salary in India?
Varies based on experience, location, and skills. Check job sites like Glassdoor or Indeed for current data.