In our modern digital era, cybersecurity threats never stand still, and ethical hackers are the front line of defense. They assist organizations in finding and repairing security flaws before bad guys can take advantage of them. It’s an exciting and fulfilling career as ethical hacker in India with great prospects for development and good pay. If cybersecurity and solving puzzles are your passions, then becoming an ethical hacker could be just the right career choice.
What is Ethical Hacking?
Ethical hacking is a legitimate process of probing systems, networks, or apps to identify security weaknesses. As opposed to malicious hackers, an ethical hacker is legitimized by organizations to identify and patch loopholes before they can be exploited. The aim is to improve cybersecurity defenses, minimize threats, and protect data. Ethical hacking is an integral component of cybersecurity strategy in today’s world, and ethical hackers are instrumental in ensuring the online security of corporations and governments alike.
What Do Ethical Hackers Do?
An ethical hacker is employed to act like an evil hacker but with integrity and purpose. His mission is to test the security of an organization’s cyber defenses within the law by trying to hack into its systems just as an actual attacker would. The difference? They do it in order to find and repair vulnerabilities, rather than exploit them.
Their day-to-day work entails:
- Conducting penetration testing and vulnerability assessments
- Discovering vulnerabilities in networks, applications, and infrastructure
- Recommendation and deployment of security upgrades
- Securing sensitive information against unauthorized access
- Verifying systems adhere to cybersecurity best practices and regulatory compliance
Ethical hackers operate in all industries, private industry, government, and even defense agencies providing protection for critical information, digital assets, and national security from would-be attackers.
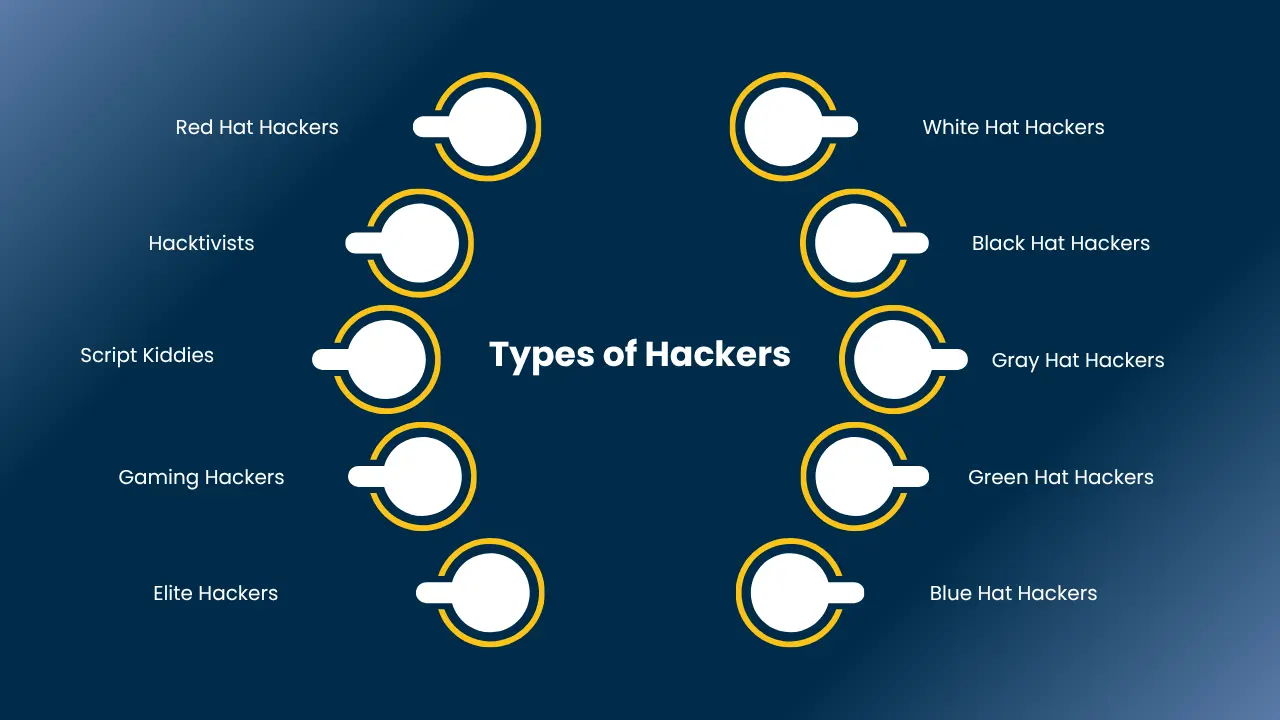
Types of Hackers
Not all hackers are created equal. Although the hacker label is frequently negative, most hackers such as an ethical hacker hijack systems to secure them, not take advantage of them. Let’s discuss the main types of hackers depending on their intention and method:
1. White Hat Hackers (Ethical Hackers)
These are cybersecurity experts who test systems legally for their vulnerabilities. An ethical hacker employs the same resources as cybercriminals but for the greater good finding and patching vulnerabilities before they can be used against them.
2. Black Hat Hackers
These people hack illegally, typically to steal information, distribute malware, or create chaos. They pose an immediate threat to cybersecurity and are usually the reason why ethical hackers are employed in the first place.
3. Gray Hat Hackers
Gray hat hackers work in a place of legal grayness. They can break into systems without consent but don’t necessarily have ill intentions. Sometimes they report vulnerabilities but may charge money for it afterward.
4. Green Hat Hackers
These are newbies or wannabe hackers. They’re inquisitive and interested in learning, often on a path to becoming either white hat or black hat hackers based on their purpose and mentorship.
5. Blue Hat Hackers
It speaks of two categories:
Inexperienced hackers for revenge or disruption without great talent.
Security professionals employed to stress-test applications (e.g., Microsoft’s BlueHat events).
6. Red Hat Hackers
Sometimes referred to as vigilante hackers, they actually seek out black hat hackers and try to take them down sometimes with violent or illegal means.
7. Hacktivists
Hackers who break into networks for the purpose of promoting political or social agendas. Their activities range from leaking confidential information to website defacement.
8. Script Kiddies
These are novice hackers who employ pre-made hacking tools without knowing much about them. They are less of a threat but are still a cybersecurity issue.
9. Gaming Hackers
These hackers take advantage of vulnerabilities in video games for the purpose of obtaining unequal benefits or stealing user data, such as personal and payment information.
10. Elite Hackers
The most proficient and advanced hackers, professional hackers are capable of identifying vulnerabilities unknown to professional experts as well. While some of them are employed as ethical hackers, others operate in secret mode.
Also Read: Top 10 Ethical Hacking Course in Delhi: Duration & Certification
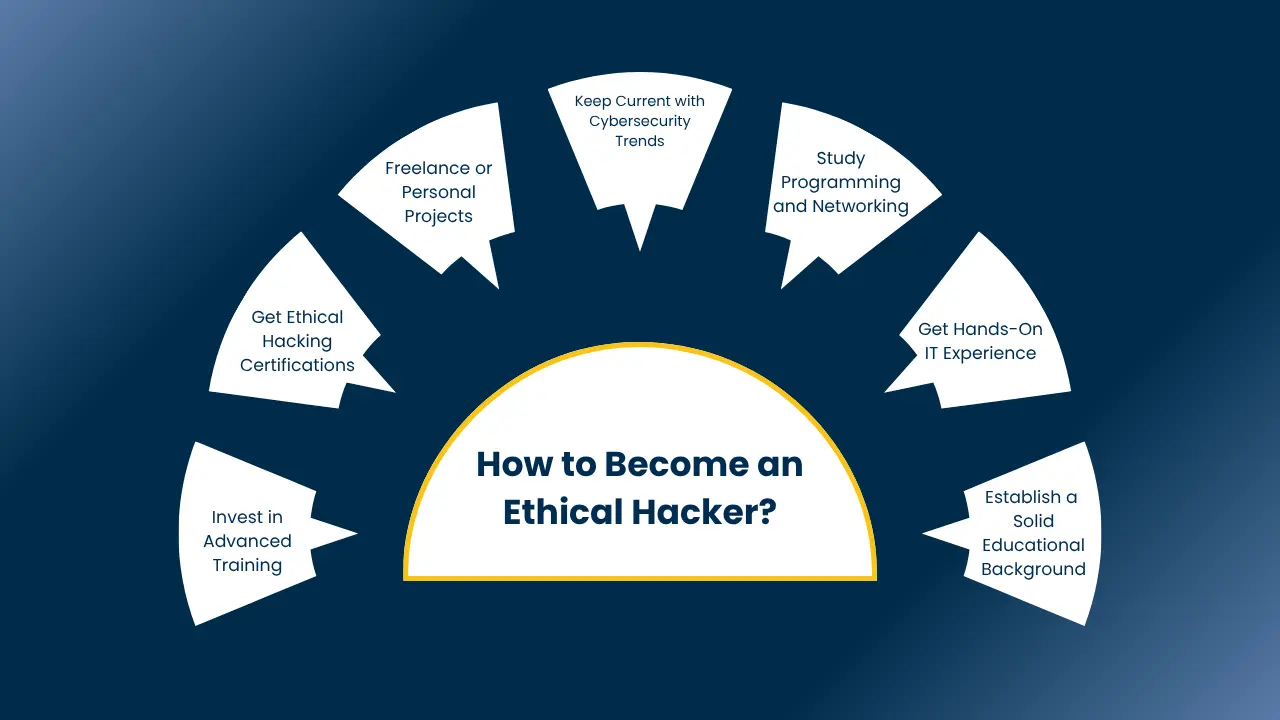
How to Become an Ethical Hacker?
Inquiring about how do you become an ethical hacker? Becoming an ethical hacker is a combination of education, hands-on experience, and lifelong learning. Here’s a step-by-step guide to embark on:
1. Establish a Solid Educational Background
Begin with a computer science, IT, or cybersecurity degree or diploma. A formal degree may not always be required, but it goes a long way to teach you systems, networks, and programming fundamentals for any ethical hacker.
2. Get Hands-On IT Experience
Start your career in network support, system administration, or security operations jobs. These jobs introduce you to actual IT environments and typical security issues.
3. Study Programming and Networking
Knowledge of coding languages such as Python, Java, or C++, and expertise in networking principles (TCP/IP, DNS, firewalls) is essential to conduct successful penetration tests.
4. Keep Current with Cybersecurity Trends
Cyber threats change quickly. Subscribe to cybersecurity blogs, pay attention to industry news, and go to conferences such as Black Hat or DefCon to keep current.
5. Freelance or Personal Projects
Try freelance penetration testing jobs or bug bounty programs to create a portfolio. Practice in real life not only sharpens your skills but also demonstrates your ability to potential employers.
6. Get Ethical Hacking Certifications
To become credible and advance your career opportunities, certifications such as the Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) are crucial. They confirm your skills and demonstrate to employers your commitment to cybersecurity.
7. Invest in Advanced Training
Take specialized bootcamps or master’s degrees in cybersecurity to further your knowledge and have access to hands-on labs and mentorship-driven training. By doing so, you can establish a fulfilling profession as an ethical hacker with the tools and mindset to secure digital systems.
How Ethical Hacking Helps Cybersecurity?
With increasingly sophisticated cyber attacks, ethical hackers are more important than ever to modern cybersecurity. They detect system vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious hackers, allowing organizations to get one step ahead.
Ethical hackers uncover potential weaknesses that might be overlooked by automated tools by simply modeling actual attacks. Their efforts are invaluable to companies, governments, and institutions looking to safeguard confidential data, ensure compliance, and avoid breaches.
From banks and accounting firms to healthcare organizations and utilities, ethical hackers are working to protect digital infrastructure in every sector. Ethical hacking isn’t just a back-office function anymore it’s a strategic imperative in this digital age.
Also Read: Best Certified Ethical Hacking Courses to Join in Andhra Pradesh
Ethical Hacker Demand
As cyberattacks increase annually, the need for professional ethical hackers has never been more acute. Organizations worldwide are actively recruiting experts who can find system vulnerabilities before malicious hackers can.
Leading organizations such as Google, IBM, Synack, and Raxis hire ethical hackers on a regular basis to protect their network. A quick perusal of LinkedIn yields thousands of job postings, including opportunities at top brands such as Bank of America, Citi, JetBlue, and even the NFL.
Whether you’re working in finance, healthcare, technology, or government, employers need certified ethical hackers to safeguard information and maintain compliance. If you’re looking for a career as an ethical hacker in India or around the world, the possibilities are immense and expanding.
Common Careers in Ethical Hacking
A career as an ethical hacker offers access to numerous high-needed careers in cybersecurity. Depending on how many years you have under your belt and which certifications you have, you can seek careers such as:
1. Penetration Tester: Mimics actual attacks to discover system vulnerabilities.
2. Vulnerability Assessor: Discovers and analyzes security gaps in networks and applications.
3. Information Security Analyst: Sees to it that IT infrastructure is safe from attacks.
4. Security Analyst: Concentrates on threat detection, response, and prevention.
5. Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) A specialist who has been certified to legally hack systems and enhance their defenses.
6. Security Consultant: Expert advisor to firms regarding the protection of their digital assets.
7. Security Engineer/Architect: Develops secure systems and enforces protection policies.
8. Information Security Manager: Manages teams and directs an organization’s security stance.
These positions provide good career advancement and lucrative ethical hacker salary packages in India and worldwide.
Key Skills Required for Ethical Hackers
To become an ethical hacker, you require more than curiosity you require a hacker’s mindset and a solid technical foundation. Whether you are looking for a certified ethical hacker course or searching for ethical hacker jobs in India, these are the skills to learn:
Thorough knowledge of networking, operating systems (Windows, Linux, macOS), and system architecture
- Understanding of contemporary security protocols and tools
- Skill in ethical hacking stages: reconnaissance, scanning, gaining access, retaining access, and erasing tracks
- Hands-on skill to detect vulnerabilities and mimic actual attacks ethically
- Encryption, cryptography, and password-cracking methodologies knowledge
- Knowledge of prevalent threats such as phishing, trojans, identity theft, insider attack, and ways to counteract them
- Proficiency in erasing digital footprints upon penetration testing
- High ethical foundation and adherence to professional standards
- Knowledge in Python, SQL, PHP, Java, C, or C++ is a significant asset
Regardless of whether you’re learning how to become ethical hacker after 12th or upskill as an IT professional, these skills are the building blocks for long-term success.
Also Read: Top 7 Scanning Tools in Ethical Hacking and their Types in 2025
Ethical Hacker Salary Statistics
The salary of an ethical hacker depends on experience, position, location, and company. Nevertheless, one thing is certain this is a well-paid and sought-after career option.
Here are some current salary figures:
- ZipRecruiter: $119,895/year (Penetration Tester)
- CyberSeek: $131,123/year (Penetration & Vulnerability Tester)
- Salary.com: $110,184/year (Ethical Hacker)
Aside from full-time positions, freelance ethical hackers, particularly bug bounty hunters, can command substantial pay for hunting down vulnerabilities for private businesses and government institutions.
For those pursuing an ethical hacker salary in India, entry-level professionals can earn ₹4–6 LPA, while experienced ethical hackers may command over ₹15 LPA. The ethical hacker salary per month can range from ₹35,000 to ₹1.25 lakh or more depending on the role and certifications.
Whether you’re just starting or already skilled, a career as an ethical hacker in India offers both financial rewards and long-term stability.
Ethical Hacker Certifications
Certifications are crucial to building credibility and landing top ethical hacker jobs in India and abroad. They validate your skills and show employers you’re serious about cybersecurity.
Some of the most respected ethical hacking and cybersecurity certifications include:
1. Certified Ethical Hacker (C|EH): Offered by EC-Council, it’s one of the most in-demand credentials for ethical hackers.
2. CompTIA Security+: A foundational certification ideal for beginners starting their ethical hacking journey.
3. Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): Known internationally for senior-level security leadership positions.
4. Certified Information Security Manager (CISM): Concentrates on the management of risk and governance.
5. Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA): Suitable for those who are interested in audit, control, and assurance.
6. SANS/GIAC Certifications: Famous for extreme technical expertise in various domains of cybersecurity.
Though a master’s in cybersecurity is not a requirement, pursuing one can provide you with a competitive advantage particularly in management positions. Enhanced education provides practical, real-world expertise and makes your resume more valuable in the employment sector.
If you ask yourself how do you become an ethical hacker or how one achieves success in this profession, these certifications are your launching point.
Read More: What is Footprinting in Ethical Hacking? Which Tool is Best for You?
How Orbus Can Help in Becoming an Ethical Hacker?
At Orbus Cybersec Trainings, we don’t only educate you on ethical hacking—we train you for an actual career in cybersecurity. Our Certified Ethical Hacker program is crafted by experts to give you the skills and attitude needed to think like a hacker and behave like a professional. You’ll get first-hand experience with simulated attacks, labs, and projects that simulate real-world threat situations.
Whether you are a student interested in learning about becoming an ethical hacker after 12th or a working professional looking to make a career change, Orbus has a customized path for you. Our instructors possess extensive industry experience, and our courseware is aligned with leading certifications such as CEH, CompTIA Security+, and more.
Additionally, we provide:
- Adaptive learning modes (online/offline/hybrid)
- Industry-standard certification guidance
- Resume preparation and placement support
- Interview preparation and career guidance
- An expanding alumni network with job referrals and assistance
By attending Orbus, you’re not only learning you’re building a future-proof, in-demand cybersecurity career. Begin your path to becoming an expert ethical hacker today and be the best ethical hacker in the world.
Conclusion
Being an ethical hacker involves more than the ability to hack into systems it involves defending them. As cyber attacks continue to mount, ethical hackers are invaluable in securing digital information and stopping data breaches. Combine the right skills, certifications, and real-world experience, and you have the ability to create a fulfilling career in one of the hottest fields of cybersecurity.
Whether you’re beginning from the ground up or making a career transition, Orbus Cybersec Trainings can guide you to learn ethical hacking and become a skilled professional in the job market. Hands-on training, expert instructors, and job-enabled certifications make your journey towards becoming a certified ethical hacker start here. Make the move join Orbus today and safeguard the digital tomorrow.