Ethical hacking has come a long way with the rise of automated tools that make security testing faster and more efficient. It plays an important role in helping organizations safeguard their systems and data against cyber attacks. Using certified ethical hacker tools not only strengthens security but also enhances the skills of security teams. Incorporating ethical hacking into standard security practices helps to identify vulnerabilities before being exploited. With growing cyber risks, it has become important to learn to use common tools used by ethical hackers to remain in the lead.
In this blog, we will help you understand how these tools for ethical hackers work, and why they are important, and get you familiar with the top 40 ethical hacking tools that professionals use today.
What Are Ethical Hacking Tools and Software?
Ethical hacking tools and software are the type of programs used by hackers to find and fix security flaws in systems, networks, and applications. These tools for ethical hackers, also called white-hat hackers, help identify vulnerabilities before criminals exploit or take advantage of them. As cyberattacks increase, companies use certified ethical hacker tools to protect their data. In Q2 2024, businesses experienced 1,636 weekly cyberattacks per week, which is a 30% year-over-year increase. To stay safe, organizations today put much trust in such tools to avoid breaches and strengthen security.
The tools used by ethical hackers include network sniffers, password crackers, and vulnerability scanners. These ethical hacking tools and techniques help find security gaps and fix them before attackers can strike them. A strong ethical hacker toolkit helps companies track suspicious activities, stop threats, and build stronger protection. The best ethical hacker tools keep businesses safe from evolving online dangers. These toolkits help increase security, avoid breaches, and protect sensitive data, thus making them a must-have for every organization.
Why Is Hacking Software Important for Ethical Hackers?
Hacking software is a valuable tool for ethical hackers to find and fix security flaws before criminals take advantage. Here’s why ethical hacking tools and techniques are important for their work:
Identifies Security Flaws:
Hacking software assists ethical hackers in discovering vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and applications. It enables them to identify threats before attackers get the chance to do so, keeping data safe.
Simulates Real-World Attacks:
Certified ethical hacker tools are operated by hackers to conduct simulated attacks to determine the strength of defenses in a system. This improves security measures.
Improves Vulnerability Testing:
Tools used by ethical hackers make it easier to scan networks and applications for loopholes. Fixing these gaps avoids data breaches.
Expands Cybersecurity Skills:
Through ethical hacking tools and techniques, hackers make their skills better. They learn how to protect systems against evolving threats.
Strengthens Compliance and Protection:
Hacking software helps businesses in complying with data protection rules like HIPAA and GDPR. It also helps reduce the chances of unwanted and expensive security breaches.
Increases Efficiency:
A good ethical hacker toolkit helps automate security testing, which saves time and makes the process much faster for the hacker. This helps them identify and resolve problems quickly.
Prevents Major Cyberattacks:
Employing the best ethical hacker tools helps stop serious breaches immediately. This protects sensitive information and prevents business losses.
Also Read: Top 10 Penetration Companies in India & Future Trends in Testing
Top Ethical Hacking Tools to Watch Out For in 2025
As cyberattacks become more and more complicated, ethical hackers rely on powerful tools to protect systems. Here are the top 40 ethical hacking tools for ethical hackers and their features to look out for in 2025:
1. Invicti
Invicti is a web security scanner that finds vulnerabilities in web apps and services.
- Uses Proof-Based Scanning for accurate results
- Needs minimal setup and is scalable
- Detects custom 404 error pages and URL rewrite rules
- REST API for easy integration with bug-tracking systems
- Scans over 1,000 web apps in 24 hours
2. Fortify WebInspect
Fortify WebInspect is an automated tool for testing web app security.
- Finds vulnerabilities in running web apps
- Offers detailed stats and reports during scans
- Allows novice testers to access pro-level testing features
- Helps with risk oversight and compliance management
3. Cain & Abel
Cain & Abel is a useful tool for recovering lost passwords and sniffing networks.
- Helps recover MS Access passwords
- Sniffs network traffic
- Uncovers hidden password fields
- Cracks encrypted passwords using brute-force and dictionary attacks
4. Nmap (Network Mapper)
Nmap is a network scanning tool for finding services and hosts.
- Discovers network services and hosts
- Creates detailed network maps
- Detects OS types and vulnerabilities
- Adapts to network conditions during scans
5. Nessus
Nessus is a vulnerability scanner for detecting security flaws.
- Finds unpatched services and misconfigurations
- Detects weak or default passwords
- Identifies various system vulnerabilities
- Recommended for non-enterprise use
6. Nikto
Nikto is a web server scanner that spots security issues.
- Scans web servers for outdated software
- Identifies over 6,400 dangerous files or CGIs
- Checks for version-specific problems
- Detects misconfigured or insecure files
7. Kismet
Kismet is an effective tool for testing and monitoring wireless networks.
- Detects hidden and non-beaconing networks
- Sniffs and collects wireless packets
- Supports raw-monitoring mode
- Runs on Linux and sometimes Windows
8. NetStumbler
NetStumbler is a Windows-based tool for detecting wireless networks.
- Finds Wi-Fi access points (AP)
- Detects network interference
- Measures signal strength
- Identifies unauthorized access points
9. Acunetix
Acunetix is an automated tool for finding web vulnerabilities.
- Detects over 4,500 web security flaws
- Supports JavaScript, HTML5, and single-page apps
- Integrates with other platforms
- Prioritizes risks based on data
10. Netsparker
Netsparker is a tool that mimics hackers to find web vulnerabilities.
- Identifies SQL injection and cross-site scripting issues
- Verifies vulnerabilities automatically
- Reduces false positives
- Saves time by removing the need for manual checks
11. Intruder
Intruder is an automated scanner that finds and fixes cybersecurity flaws.
- Detects missing patches, misconfigurations, and web app issues
- Integrates with Slack, Jira, and cloud providers
- Prioritizes results based on context
- Scans for the latest vulnerabilities automatically
12. Volatility
Volatility is an open-source tool for memory forensics and digital investigations.
- Analyzes RAM dumps for hidden processes and malware
- Helps with cyber incident investigations
- Extracts running processes, network connections, and registry hives
13. Metasploit
Metasploit is a framework for penetration testing and developing exploit codes.
- Works on multiple platforms
- Ideal for finding security flaws
- Great for creating evasion and anti-forensic tools
14. Aircrack-Ng
Aircrack-Ng is a command-line tool for testing and attacking Wi-Fi networks.
- Exports data to text files
- Cracks WEP and WPA2-PSK keys
- Supports Windows, Linux, and multiple platforms
15. Wireshark
Wireshark is a packet analysis tool for inspecting network traffic.
- Performs live and offline packet analysis
- Works across platforms
- Uses color coding to simplify packet tracking
16. OpenVAS
OpenVAS is a tool for large-scale vulnerability scans.
- Performs authenticated and unauthenticated testing
- Supports industrial protocols
- Allows performance tuning and detailed scanning
17. SQLMap
SQLMap is an open-source tool for detecting and exploiting SQL injection flaws.
- Powerful detection engine
- Executes arbitrary commands
- Supports MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, and more
18. Ettercap
Ettercap is a free tool for sniffing network traffic and protocol analysis.
- Filters content in real-time
- Sniffs live connections
- Analyzes networks and hosts
- Supports active and passive protocol dissection
19. Maltego
Maltego is a tool for data mining and link analysis.
- Runs on Windows, Linux, and Mac OS
- Performs real-time data gathering
- Displays results in visual, easy-to-read graphs
20. Burp Suite
Burp Suite is an effective security-testing tool for web vulnerability scans.
- Allows scan scheduling and repeating
- Uses out-of-band techniques
- Offers CI (Continuous Integration) support
21. John the Ripper
John the Ripper is a free password-cracking tool used to test weak passwords.
- Includes multiple password crackers in one bundle
- Performs dictionary attacks
- Tests various encrypted passwords
22. Angry IP Scanner
Angry IP Scanner is a free tool for scanning IP addresses and ports.
- Exports results in different formats
- Offers a command-line interface
- Extensible with multiple data fetchers
23. SolarWinds Security Event Manager
SolarWinds Security Event Manager detects threats and monitors security policies.
- Built-in integrity monitoring
- User-friendly dashboard and interface
- Tracks log files and sends instant alerts
24. Traceroute NG
Traceroute NG is a network path analysis tool that identifies hostnames and IP addresses.
- Supports both IPv4 and IPv6
- Detects path changes and sends alerts
- Allows continuous network probing
25. LiveAction
LiveAction is a tool for diagnosing and resolving network issues quickly.
- Easy-to-use workflow
- Automates data capture for faster response
- Provides deep packet analysis
- Onsite deployment for appliance use
26. QualysGuard
QualysGuard is a cloud security tool for identifying vulnerabilities.
- Globally trusted for IT security
- Scalable, end-to-end solution
- Real-time data analysis
- Responds to live threats
27. Responder
Responder captures and manipulates local network queries.
- Gathers credentials through network poisoning
- Runs silently in the background
- Captures user credentials from insecure services
28. Hashcat
Hashcat is a powerful password-cracking tool.
- Open-source and multi-platform
- Supports distributed cracking networks
- Automatic performance tuning
29. L0phtCrack
L0phtCrack is a password recovery and auditing tool for local networks.
- Customizable and easy to use
- Fixes weak passwords by forcing resets
- Uses multi-core and multi-GPU support
30. Rainbow Crack
Rainbow Crack is a password-cracking tool using rainbow tables.
- Runs on Windows and Linux
- Offers command-line and graphic interfaces
- Uses a unified rainbow table format
31. IKECrack
IKECrack is an open-source authentication-cracking tool used for brute-force and dictionary attacks.
- Strong focus on cryptography
- Suitable for both personal and commercial use
32. Sboxr
Sboxr is an open-source tool for vulnerability testing and creating custom security scanners.
- Easy-to-use GUI-based interface
- Supports Ruby and Python
- Generates reports in RTF and HTML formats
- Checks over two dozen web vulnerabilities
33. Medusa
Medusa is a fast, brute-force parallel password-cracking tool.
- Flexible user input options
- Supports remote authentication services
- Great for thread-based parallel testing
34. Hping3
Hping3 is a network scanning and security auditing tool.
- Creates custom TCP/IP packets
- Assesses open, closed, or filtered ports
- Useful for Denial of Service (DoS) Testing
35. Zenmap
Zenmap is the official Nmap Security Scanner with a graphical interface.
- Tracks new or downed hosts and services
- Displays graphical, interactive results
- Draws topology maps of discovered networks
36. Recon-ng
Recon-ng is a Python-based information-gathering framework.
- Reduces time spent harvesting open-source data
- Includes multiple modules and database interaction
- Centralizes data collection into a single source
37. njRAT
njRAT is a remote access trojan used for unauthorized system access.
- Grants remote access to file systems
- Allows attackers to control multiple services
- Designed to enter systems without permission
38. Fping
Fping is an open-source network diagnosis tool.
- Sends ICMP pings to multiple hosts simultaneously
- Faster than traditional ping tools
- Displays IP addresses of available machines
39. SuperScan
SuperScan is a free multi-functional port scanner.
- Detects open TCP and UDP ports
- Performs host discovery and trace routing
- Includes whois, ping, and ICMP traceroute queries
40. Nexpose
Nexpose is a paid vulnerability scanner with a 30-day trial.
- Scans network assets, databases, and web apps
- Offers real-time visibility into vulnerabilities
- Provides prioritized remediation reports
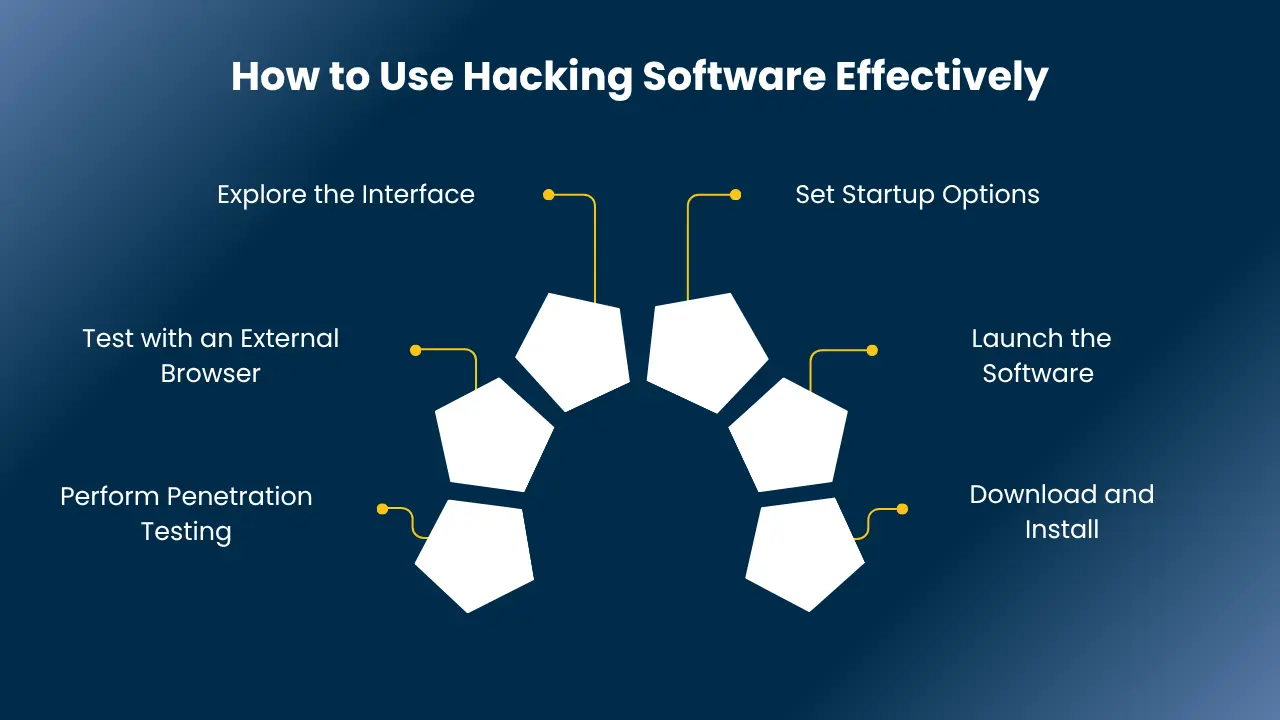
How to Use Hacking Software Effectively
Using hacking software properly is important for finding and fixing security flaws. Here’s how you can do it:
1. Download and Install:
Get the hacking software you want, such as certified ethical hacker tools, from a trusted source. Install it on your system.
2. Launch the Software:
Open the program once it’s installed and running.
3. Set Startup Options:
Choose the settings or startup options based on the ethical hacking tools and techniques you want to use.
4. Explore the Interface:
Check out the tool’s features and options. Learn how to navigate it properly.
5. Test with an External Browser:
Use a browser to test the tool’s scanning and security functions.
6. Perform Penetration Testing:
Use the software to scan websites, detect vulnerabilities, and perform penetration testing. This helps you find weak spots and strengthen security.
These steps will allow you to make the most of the common tools used by ethical hackers and boost your cybersecurity skills.
Read More: Best SailPoint IdentityIQ Interview Questions
How Orbus Can Help You Become an Ethical Hacker
At Orbus International, we help you become a skilled ethical hacker through our Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) training program. We offer practical, hands-on learning to teach you how to use the latest ethical hacking tools and techniques effectively. Our course covers everything from common tools used by ethical hackers to advanced certified ethical hacker tools for identifying and fixing security flaws.
Why Choose Orbus?
- Industry-related Training: We cover all essential tools used by ethical hackers, including penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security auditing.
- Hands-on Learning: You’ll get practical experience with real-world ethical hacker toolkit applications.
- Flexible Schedules: We offer day, evening, and weekend classes to fit your routine.
- Expert Guidance: Learn from industry professionals with years of experience.
- Career-Boosting Skills: Gain job-ready skills that make you a valuable asset in the growing field of cybersecurity.
At Orbus, we are committed to helping you build a strong foundation in ethical hacking and excel in your cybersecurity career.
Conclusion
Cyber threats are increasing every day, making it more important for companies to protect their data. This is why many organizations are now hiring certified ethical hackers to find and fix security flaws before attackers can exploit them. Using tools for ethical hackers, companies can spot weaknesses, strengthen their defenses, and avoid costly data breaches.
At Orbus International, we offer expert training programs that teach you how to use certified ethical hacker tools effectively. You’ll learn common tools used by ethical hackers and ethical hacking tools and techniques through real-world scenarios. This hands-on approach helps you build the skills needed to tackle modern cyber threats.
Get started with Orbus today and take the first step toward becoming a skilled ethical hacker!