In the contemporary world, it is important to secure network infrastructures. Firewall administrators are therefore very important in this field. Their functions include installing, maintaining, and monitoring firewall systems. They serve as a shield against intruders and cyber-attacks that threaten organizations. Cyber-attacks have been rising at an incredible rate. Due to this, there is an increase in the demand for Firewall administrator professionals, and rightly so. We will discuss the firewall administrator roles and responsibilities, training, career opportunities, and maybe also touch on what are the most crucial skills in becoming a Firewall administrator. It is a how-to for those who are ready to thrive in the dynamic landscape of penetration testing in cyber security.
Who is a Firewall Administrator?
A firewall administrator constitutes a critical team member of the cybersecurity staff for penetration testing companies in India. It is his/her responsibility to allow or disallow network traffic through the firewall’s management console according to predetermined security policies appropriate for the business. His objective is to deny payment to every unauthorized entity, while only permitting authorized entities access to data. They are the network security mangers and their responsibility is to enable or disable firewall policies and security modifications in such a manner that the organization’s systems become secure, compliant, and free from threats.
What Do Firewall Administrators Do?
When it comes to protecting a company’s network, firewall administration basics are the first line of defense. Setting up, maintaining, and monitoring firewall systems around-the-clock to let only trusted traffic through and stop threats from causing harm is the main focus of their work. Lets check out the firewall administrator job description:
1. Setting Up and Managing
- Applying Firewall Rules: They establish and apply rules for what types of information are allowed to enter or leave the network according to organizational security policies.
- Firewall Device Management: Software- or hardware-based, they ensure that all firewall systems are operating and properly configured.
- User Access Control: The administrators assign the right roles and permissions and determine who gets to access firewall management systems.
- Change Management: All modifications to the firewall configuration are properly documented and approved, maintaining documented change control procedures.
- Monitoring and Security Log Analysis: To identify any unusual activity or threats, they continuously review firewall logs.
- Threat Detection: Firewall managers monitor traffic in real time and check for any unusual activity.
- Security Audits: Through updated configurations and documentation, internal and external security audits are simplified.
- Vulnerability management: They continually search for and eliminate any vulnerability in the firewall or the network itself.
2. Observance and Reaction to Incidents
- Policy Enforcement and Compliance: The administrators take good care to make sure that the configuration of the firewall adheres to external as well as internal policies.
- Incident Handling: They are primarily responsible for investigating and rectifying any incident or unusual activity.
- Cooperation and Ongoing Education
- Backup and Restoration: In case of system failure, rapid recovery is facilitated by regular configuration backups.
- Teamwork: While performing larger network security projects, they work closely with other IT departments.
- Keeping Up to Date: They continuously update their knowledge and skill sets since new threats are constantly emerging.
Top 12 Key Skills Required for Firewall Administrator
Technical know-how, analytical thinking, and a team player approach are all what it takes for an effective firewall administrator. On top of maintaining firewall systems, they must also be familiar with network security as a whole and how it all integrates.
1, Network Security and FireWall Administration
Understanding the proper installation and maintenance of firewalls is key. Higher-level understanding of network security concepts must be possessed by the administrators to construct strong defenses.
2. Networking & Network Configuration
Secure management of data flow requires good understanding of networking basics like TCP/IP, routing, DNS, and access control.
3. Operating Systems
Understanding of Windows, Linux, and other operating systems helps to install firewalls in different environments.
4. Virtualization & Cloud Computing
Knowledge of virtualized environments and cloud platforms like AWS or Azure becomes increasingly important as infrastructures shift towards hybrid models.
5. Scripting & Automation
Familiarity with scripting languages (e.g., PowerShell, Python) helps administrators to automate steps and enhance efficiency.
6. Patch & Security Management
Maintaining up to date with system updates and patching firewall and network infrastructure is the solution to minimizing vulnerabilities.
7. Hardware & System Integration
Understanding the physical components of a network and where firewalls integrate with other hardware is a plus.
8. Soft Skills & Professional Competencies
Problem-Solving & Analytical Thinking: Being able to swiftly diagnose issues, identify the source of the issue, and implement the remedies is important.
9. Communication & Collaboration
Firewall admins often work closely with other IT and security teams, so effective communication and collaboration are critical.
10. Compliance & Security Standards
Industry standards awareness (e.g., ISO, GDPR, or PCI-DSS) guarantees that firewall configurations comply with standards.
11. Active Directory & Access Control
User access and directory services management are crucial to secure authentication across the network.
12. Certifications
Holders of certification like CEH, CompTIA Security+, or CPENT are able to showcase demonstrated competence and build credibility.
By combining the right mix of these skills, a Firewall Administrator is capable of safely protecting an organization’s computer resources and adapt to evolving security threats.
How to Become an Firewall Administrator after Cpent Certification
Penetration testing certification india gives you a technical foundation, especially for offensive security. To transition to become a Firewall Administrator, this step-by-step guide presented in easy-to-understand and orderly fashion will guide you there.
1. Leverage CPENT Knowledge
Use your penetration testing experience to think like an attacker this allows you to set up firewalls more effectively from a defensive perspective. Employ the basics of hacking and penetration testing techniques to identify vulnerabilities in the configuration of firewalls and increase your ability to anticipate attacks.
2. Get Familiar with Firewall Tools
Gain experience with market-leading firewalls such as Cisco ASA, Palo Alto, Fortinet, pfSense, and Sophos. Learn how to design, manage, and audit firewall rules and access policies on multiple platforms.
3. Set Up Hands-On Labs
Get hands-on experience setting up firewalls in a virtual lab environment. Get experience simulating attacks and testing your firewall defenses to get real-world experience and feel confident with your configurations.
4. Deepen Your Networking Knowledge
Enrich your understanding of TCP/IP, DNS, VPNs, NAT, and other basic networking protocols. Understand how data packets move around the network and how firewalls control that traffic securely.
5. Master Traffic Analysis and Intrusion Detection
Learn about analyzing and monitoring network traffic patterns. Utilize tools such as Wireshark and Snort along with your firewall to look for anomalous behavior or potential threats.
6. Gain Real-World Experience
Look for internships, lab work, or freelance opportunities in network security or firewall management. Practical experience builds technical and problem-solving skills.
7. Obtain Specialized Certifications
Look into obtaining additional certifications such as Palo Alto Networks Certified Security Engineer (PCNSE), Cisco CCNP Security, Fortinet NSE (specifically NSE 4 and above), or even CompTIA Security+ to increase your expertise.
8. Stay Updated
Be current with the newest firewall innovations, security trends, and threat intelligence. Cybersecurity is constantly changing, and it makes you professionally ahead if you’re current.
With this path, augmented by your CPENT foundation, you’ll be ready to step into a Firewall Administrator role with confidence and drive measurable change to organizational security.
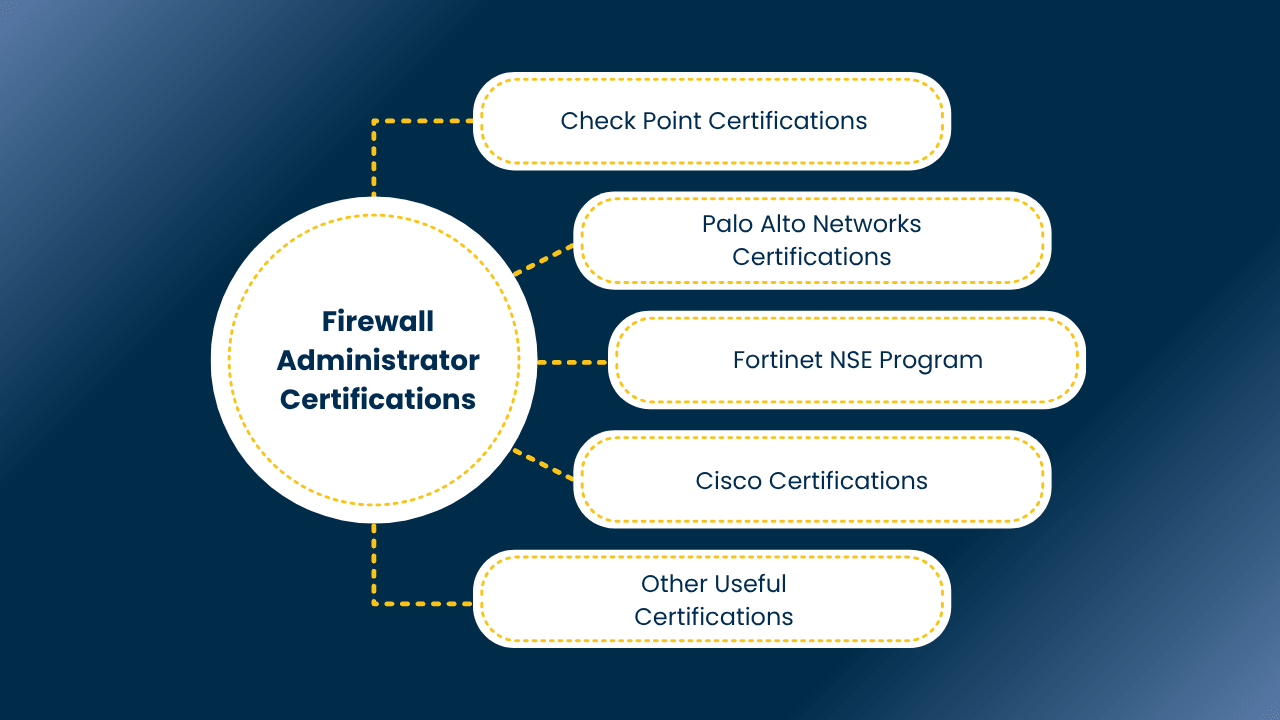
Firewall Administrator Certifications
If a career as a Firewall Administrator is in your sights, obtaining the appropriate certifications will put you firmly in the driver’s seat in terms of job competitiveness. These certifications demonstrate your proficiency in administering, configuring, and securing firewalls on multiple platforms and network infrastructures.Most of the firewalls are company-specific certifications that are based on a company’s technology such as Check Point, Palo Alto Networks, Fortinet, or Cisco. All offer a certification stream that matches your level of skill from the beginner to the expert.
1. Check Point Certifications
Check Point’s certification path is well-regarded for firewall experts. It begins with the CCSA (Check Point Certified Security Administrator R80), which addresses the fundamentals of installing, setting up, and managing firewall security policies. The CCSE (Check Point Certified Security Expert R80) follows, which explores more in-depth advanced management and troubleshooting methods. For those dealing with large-scale or extremely complex firewall infrastructures, Check Point provides the CCSM (Certified Security Master) and CCMSE (Certified Security Master Elite), both of which are intended for senior-level positions.
2. Palo Alto Networks Certifications
Palo Alto firewalls are commonly employed in business environments, and PCNSE (Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Engineer) is their most popular certification. It confirms skills in designing, implementing, and operating Palo Alto firewalls. New users may begin with the PCNSA (Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Associate), which is for simple configurations and operations.
3. Fortinet NSE Program
Fortinet’s Network Security Expert (NSE) program is a multi-level certification track. It goes from foundational knowledge (NSE 1–3) to hands-on technical know-how (NSE 4–6), and advanced solution design and implementation (NSE 7–8). It’s perfect for professionals working with FortiGate firewalls and Fortinet’s overall security infrastructure.
4. Cisco Certifications
Cisco provides the CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate), which is an entry-level certification covering the basics of networks, including firewall fundamentals. For students interested in Cisco’s Adaptive Security Appliances, there is a special ASA Certification that gives more details on deploying and managing Cisco firewalls.
5. Other Useful Certifications
While vendor certifications are essential, broader security certifications can enhance your credibility. CompTIA Security+ provides a strong introduction to general cybersecurity concepts, including firewalls. CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) is a high-level certification that validates your overall expertise in security architecture and operations.
Another solid option is GIAC Security Essentials (GSEC), which focuses on practical skills in network security and defense. All of these firewall administration certifications not only enhance your skill set but also indicate to employers that you’re committed to your position as a security professional.
Firewall Administrator Salary
In India, the average annual salary for a Firewall Administrator is around ₹10,37,000, as per recent statistics. This comes to a monthly salary of around ₹86,417. Salaries may differ depending on experience, certificates, and location. Junior positions can begin from ₹8,00,000 per annum, whereas experienced personnel may earn as much as ₹12,10,000 per year. Metro cities such as Bengaluru, Mumbai, and Pune tend to provide greater compensation levels considering the presence of tech firms.
How Orbus Can Help in Becoming a Firewall Administrator
At Orbus International, we ensure professionals are empowered with the best cybersecurity training. Our advanced firewall administration courses are crafted to impart the skills you need to be a standout performer in the key arena of network security.
| Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Network Security Training | Foundational training in network security principles, vital for understanding firewall management. |
| CPENT Certification (Pen Testing) | Focuses on penetration testing skills, allowing for deep understanding of network vulnerabilities and exploit mitigation, crucial for firewall configuration. |
| Vulnerability Assessment Training | Equips with skills to identify network weaknesses, essential knowledge for effective firewall policy implementation. |
| Real-World Skills (USPs) | Hands-on, practical training designed for immediate workplace application. |
| Industry-Recognized Certifications (USPs) | Enhances credibility and demonstrates proven expertise in network security, a core requirement for firewall roles. |
| IT Recruitment Assistance (USPs) | Helps with job placement by leveraging Orbus International’s recruiting network. |
| Fees & Duration | Vary based on a specific penetration testing course. Contact Orbus International for details. |
| USPs Summary | Practical training, respected certifications, recruitment aid, cybersecurity specialization, expert consultants. |
Conclusion
Pursuing a career as a Firewall Administrator provides an exciting and fulfilling career in the constantly changing arena of cybersecurity. The job requires technical acumen, lifelong learning, and flexibility to keep up with evolving threats. As organizations are focusing more on network security, the professionals in this field are not only highly sought after but also have competitive pay and various opportunities for growth. By gaining the appropriate certifications, developing practical skills, and keeping up with technology, individuals can set themselves up for a successful career that involves safeguarding digital assets and creating secure network environments.